YAG Laser finds application in two key areas of eye treatment – In treating angle closure glaucoma and complications of cataract surgery. In both cases, the laser treatment is a simple, short duration walk-in and walk-out procedure generally associated with excellent outcomes.
YAG Capsulotomy:
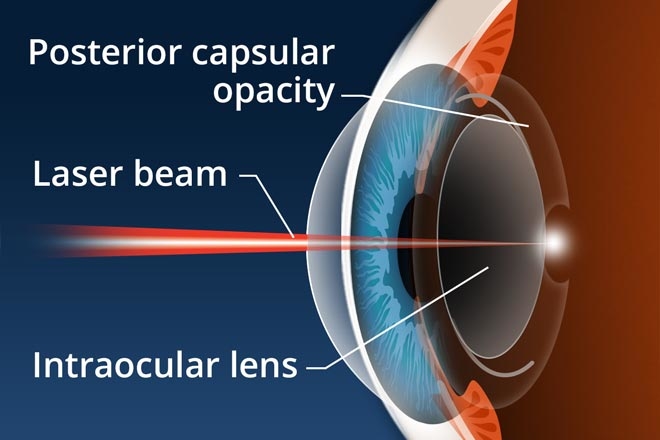
Posterior capsule opacification (PCO) is a complication that can crop up after cataract surgery. Around 10% of cataract patients have a tendency to develop PCO within two years of surgery. PCO causes them to experience cloudy vision again. The reason is that the capsule membrane which holds the synthetic lens intact grew thicker and slightly opaque. Consequently the ability of light to reach the retina is weakened resulting in dim vision.
PCO can be easily treated with a quick, painless and low risk laser procedure to restore the clear vision. In the preparatory phase, the pupil is dilated with eye drops. The patient is asked to sit and position the head on the headrest of the machine. The ophthalmologist directs the laser beam on to the rear portion of the artificial lens to detach a small circular tissue. It is common to notice a few flashes and hear some click sounds during the procedure.
It is quite natural to visualize dots, lines, circles or webs for a short while after the procedure and there is no reason to panic. Refrain from driving until the vision returns to normal state and thereafter you can get back to your routine work.
YAG Iridotomy:
Glaucoma is widely classified into two categories.
1. Open-angle glaucoma
2. Angle-closure glaucoma
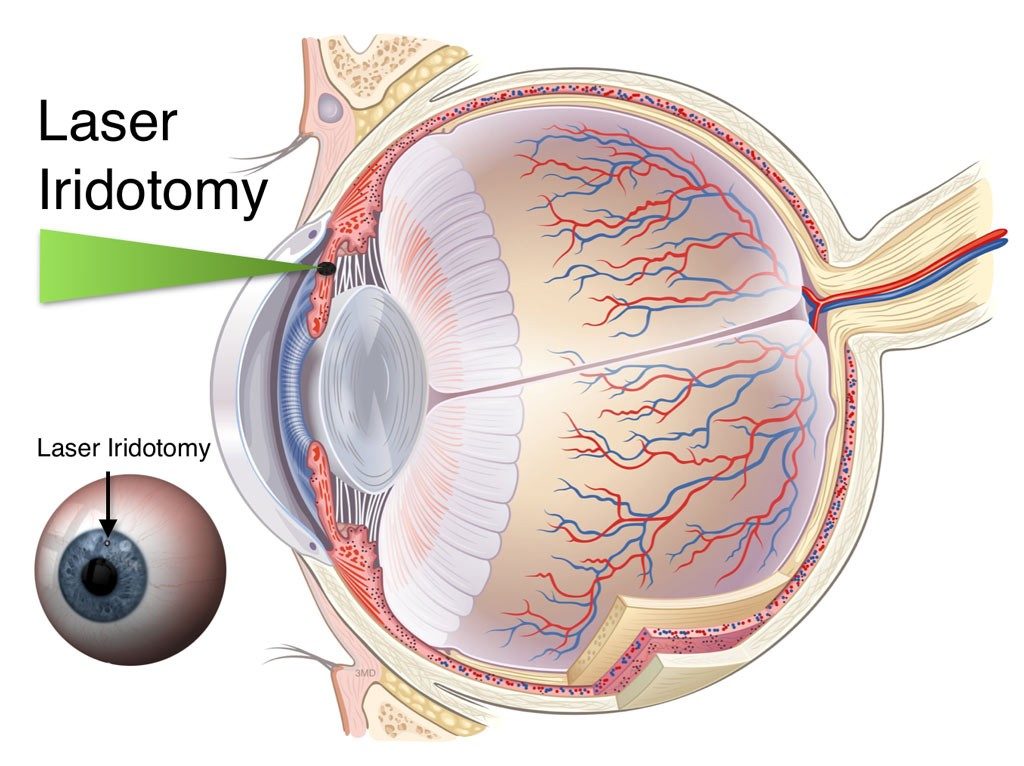
YAG laser can be used to treat the second type of glaucoma. The defect in this case is that the space between the clear part of external eye, cornea, and coloured part, namely iris, containing mesh pattern is blocked.
In the preparatory phase, the pupil is made to contract in size by instilling eye drops. Anesthetic drops may also be given for relieving the pain. The procedure widens the space by introducing a hole in the iris thereby facilitating the drainage of aqueous fluid. Thus the circulation becomes free maintaining the eye pressure and saving the optic nerve from damage. As well known, glaucoma is one of the leading cause of blindness of eye.
Possible side effects such as redness of eyes, mild headache, excessive sensitiveness to light may be experienced which will gradually disappear. The procedure can be performed in both the eyes, on the same sitting. In certain cases, repetition of the procedure or further treatment with a close follow up may be required.
